安卓中的日期和时间格式
Android 中的日期和时间使用 Java 中的 SimpleDateFormat 库进行格式化,使用 Calendar 实例帮助获取当前系统的日期和时间。当前日期和时间属于 Long 类型,可以转换为人类可读的日期和时间。在本文中,已经讨论了日期和时间值如何以各种格式格式化和显示。请看下图,了解整个讨论。
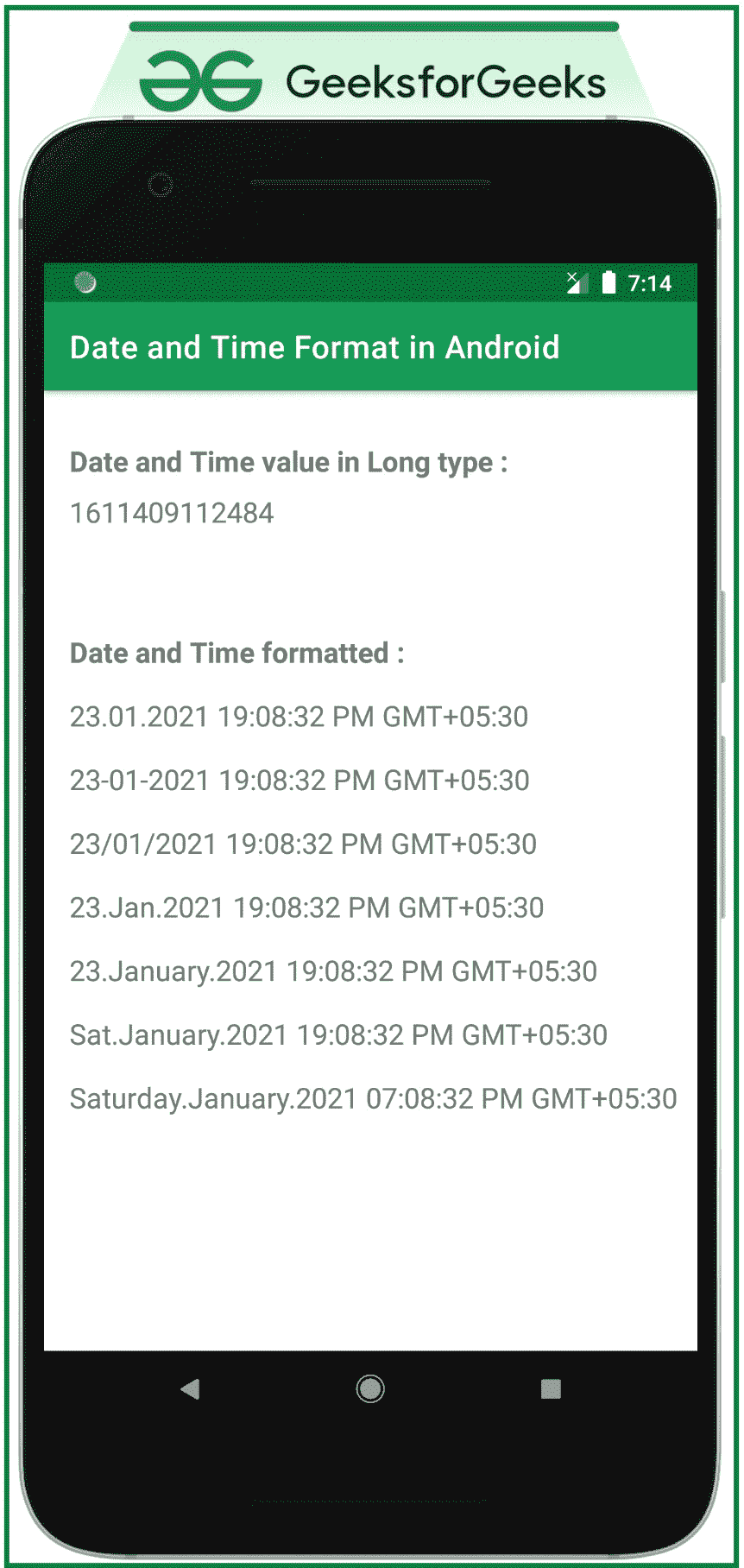
在安卓系统中格式化日期和时间的步骤
第一步:创建一个空的活动项目
- 使用安卓工作室创建一个空的活动项目。参考安卓|如何在安卓工作室创建/启动新项目?
步骤 2:使用 activity_main.xml 文件
- 包含 8 个文本视图的活动文件的主布局。一个以长整型显示当前系统日期和时间值,另一个以格式化的可读方式显示相同的日期和时间值。
- 要实现用户界面,在 activity_main.xml 文件中调用以下代码。
可扩展标记语言
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity"
tools:ignore="HardcodedText">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="16dp"
android:layout_marginTop="32dp"
android:text="Date and Time value in Long type :"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:textStyle="bold"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<!--text view to show the current
date and time in Long type-->
<TextView
android:id="@+id/dateTimeLongValue"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="16dp"
android:layout_marginTop="64dp"
android:textSize="18sp"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="16dp"
android:layout_marginTop="64dp"
android:text="Date and Time formatted :"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:textStyle="bold"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/dateTimeLongValue" />
<!--text views to show the current date and
time in formatted and human readable way-->
<TextView
android:id="@+id/format1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="16dp"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:textSize="18sp"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/textView" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/format2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="16dp"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:textSize="18sp"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/format1" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/format3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="16dp"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:textSize="18sp"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/format2" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/format4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="16dp"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:textSize="18sp"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/format3" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/format5"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="16dp"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:textSize="18sp"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/format4" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/format6"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="16dp"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:textSize="18sp"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/format5" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/format7"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="16dp"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:textSize="18sp"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/format6" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
第三步:使用 主要活动文件
了解安卓中使用 SimpleDateFormat 格式化日期和时间的方式
- 首先,创建日历的实例,并且要显示的日期和时间的期望格式被传递给简单日期格式方法。字符串应该包含以下字符,并且可以包含分隔符,如-、/等。
- 下表包括用于生成最常用的日期和时间模式的字符。
- 请参考下面的代码及其输出,以便更好地理解上表。
我的锅
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import android.os.Bundle
import android.widget.TextView
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat
import java.util.*
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
var dateTime: String
var calendar: Calendar
var simpleDateFormat: SimpleDateFormat
// register all the text view with appropriate IDs
val dateTimeInLongTextView: TextView = findViewById(R.id.dateTimeLongValue)
val format1: TextView = findViewById(R.id.format1)
val format2: TextView = findViewById(R.id.format2)
val format3: TextView = findViewById(R.id.format3)
val format4: TextView = findViewById(R.id.format4)
val format5: TextView = findViewById(R.id.format5)
val format6: TextView = findViewById(R.id.format6)
val format7: TextView = findViewById(R.id.format7)
// get the Long type value of the current system date
val dateValueInLong: Long = System.currentTimeMillis()
dateTimeInLongTextView.text = dateValueInLong.toString()
// different format type to format the
// current date and time of the system
// format type 1
calendar = Calendar.getInstance()
simpleDateFormat = SimpleDateFormat("dd.MM.yyyy HH:mm:ss aaa z")
dateTime = simpleDateFormat.format(calendar.time).toString()
format1.text = dateTime
// format type 2
calendar = Calendar.getInstance()
simpleDateFormat = SimpleDateFormat("dd-MM-yyyy HH:mm:ss aaa z")
dateTime = simpleDateFormat.format(calendar.time).toString()
format2.text = dateTime
// format type 3
calendar = Calendar.getInstance()
simpleDateFormat = SimpleDateFormat("dd/MM/yyyy HH:mm:ss aaa z")
dateTime = simpleDateFormat.format(calendar.time).toString()
format3.text = dateTime
// format type 4
calendar = Calendar.getInstance()
simpleDateFormat = SimpleDateFormat("dd.LLL.yyyy HH:mm:ss aaa z")
dateTime = simpleDateFormat.format(calendar.time).toString()
format4.text = dateTime
// format type 5
calendar = Calendar.getInstance()
simpleDateFormat = SimpleDateFormat("dd.LLLL.yyyy HH:mm:ss aaa z")
dateTime = simpleDateFormat.format(calendar.time).toString()
format5.text = dateTime
// format type 6
calendar = Calendar.getInstance()
simpleDateFormat = SimpleDateFormat("E.LLLL.yyyy HH:mm:ss aaa z")
dateTime = simpleDateFormat.format(calendar.time).toString()
format6.text = dateTime
// format type 7
calendar = Calendar.getInstance()
simpleDateFormat = SimpleDateFormat("EEEE.LLLL.yyyy KK:mm:ss aaa z")
dateTime = simpleDateFormat.format(calendar.time).toString()
format7.text = dateTime
}
}
Java 语言(一种计算机语言,尤用于创建网站)
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
TextView dateTimeInLongTextView, format1, format2,
format3, format4, format5, format6, format7;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
String dateTime;
Calendar calendar;
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat;
// register all the text view with appropriate IDs
dateTimeInLongTextView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.dateTimeLongValue);
format1 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.format1);
format2 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.format2);
format3 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.format3);
format4 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.format4);
format5 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.format5);
format6 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.format6);
format7 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.format7);
// get the Long type value of the current system date
Long dateValueInLong = System.currentTimeMillis();
dateTimeInLongTextView.setText(dateValueInLong.toString());
// different format type to format the
// current date and time of the system
// format type 1
calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("dd.MM.yyyy HH:mm:ss aaa z");
dateTime = simpleDateFormat.format(calendar.getTime()).toString();
format1.setText(dateTime);
// format type 2
calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("dd-MM-yyyy HH:mm:ss aaa z");
dateTime = simpleDateFormat.format(calendar.getTime()).toString();
format2.setText(dateTime);
// format type 3
calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("dd/MM/yyyy HH:mm:ss aaa z");
dateTime = simpleDateFormat.format(calendar.getTime()).toString();
format3.setText(dateTime);
// format type 4
calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("dd.LLL.yyyy HH:mm:ss aaa z");
dateTime = simpleDateFormat.format(calendar.getTime()).toString();
format4.setText(dateTime);
// format type 5
calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("dd.LLLL.yyyy HH:mm:ss aaa z");
dateTime = simpleDateFormat.format(calendar.getTime()).toString();
format5.setText(dateTime);
// format type 6
calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("E.LLLL.yyyy HH:mm:ss aaa z");
dateTime = simpleDateFormat.format(calendar.getTime()).toString();
format6.setText(dateTime);
// format type 7
calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("EEEE.LLLL.yyyy KK:mm:ss aaa z");
dateTime = simpleDateFormat.format(calendar.getTime()).toString();
format7.setText(dateTime);
}
}
输出:


