安卓中的简单适配器,示例
原文:https://www . geesforgeks . org/simple adapter-in-Android-with-example/
在安卓系统中,每当我们想要绑定一些从任何数据源(例如数组列表、哈希映射、SQLite 等)获取的数据时。)与 UI 组件(例如,ListView、GridView 等)一起使用。)然后适配器进入画面。基本上适配器充当了用户界面组件和数据源之间的桥梁。这里简易适配器是适配器的一种。它基本上是一个简单的适配器,可以将静态数据映射到我们的 XML 文件(用户界面组件)中定义的视图,并用于定制列表或网格项目。这里我们使用了一个映射的数组列表(例如 hashmap、可变映射等)。)进行数据备份。数组列表中的每个条目对应于列表中的一行。地图包含每行的数据。现在要显示该行,我们需要一个视图,我们使用它来指定一个自定义列表项文件(一个 XML 文件)。
简单适配器的一般语法
SimpleAdapter ( 上下文上下文,列表 <?延伸地图 < 字符串,?> >数据, int 资源, String [] from, int [] to)
**这里上下文、数据、资源、自和至是五个参数 * *
例子
下面给出了一个示例图像,以了解本文中要做什么。在这个项目中,我们将制作这个应用程序,其中有一些水果的列表,列表的每一行都有一个水果图像和名称。请注意,我们将在 Kotlin 和 Java 语言中实现同一个项目。现在你选择你喜欢的语言。
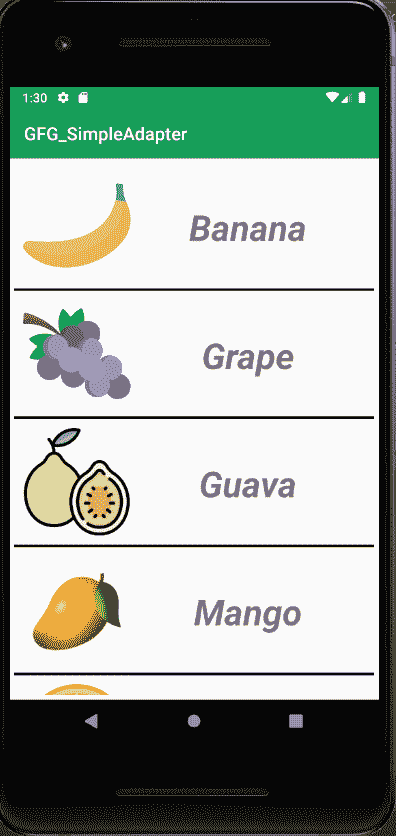
逐步实施
第一步:创建新项目
打开安卓工作室>新建项目 >选择一个空活动> 给出一个项目名称(这里我们的项目名称是“ GFG_SimpleAdapter ”)。

***这里你可以选择你喜欢的 Kotlin 或者 Java,根据你的选择选择 API 级别。
- 创建项目成功后,请将一些图片粘贴到 res 目录中的可绘制文件夹中。现在你可以使用我在我的项目中使用的相同的图片,否则你可以选择你自己选择的图片。要下载相同的图片,请点击下面的链接:*
*请注意,它是可选的* * ***
*步骤 2:使用 activity_main.xml 文件*
在 activity_main.xml 文件中,在 RelativeLayout 内创建一个列表视图。下面是 activity_main.xml 文件的代码。
可扩展标记语言
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<!--Creating a ListView-->
<ListView
android:id="@+id/listView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:divider="#000000"
android:dividerHeight="3dp"
android:padding="5dp" />
</RelativeLayout>
*activity_main.xml 接口:*

*第三步:创建另一个 XML 文件(命名为 list_row_items),并为 ListView 的每一行创建 UI*
创建一个新的布局资源文件,并将其命名为列表 _ 行 _ 项目。
下面是 list_row_items.xml 文件的代码。
可扩展标记语言
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<!--Creating a ImageView-->
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView"
android:layout_width="120dp"
android:layout_height="120dp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:scaleType="fitCenter"
android:src="@drawable/ic_launcher_background" />
<!--Creating a TextView-->
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="40dp"
android:layout_marginRight="20dp"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/imageView"
android:gravity="center"
android:padding="5dp"
android:text="Text View"
android:textColor="#808080"
android:textSize="40sp"
android:textStyle="bold|italic" />
</RelativeLayout>
*list_row_items.xml 接口:*

*步骤 4:使用主活动文件*
在这里,我们将向您展示如何在 Java 和 Kotlin 中实现 SimpleAdapter。现在你选择你的首选。以下是主活动文件的代码。代码中添加了注释,以更详细地理解代码。
Java 语言(一种计算机语言,尤用于创建网站)
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.SimpleAdapter;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
ListView listView;
// creating a String type array (fruitNames)
// which contains names of different fruits' images
String fruitNames[] = {"Banana", "Grape", "Guava", "Mango", "Orange", "Watermelon"};
// creating an Integer type array (fruitImageIds) which
// contains IDs of different fruits' images
int fruitImageIds[] = {R.drawable.banana,
R.drawable.grape,
R.drawable.guava,
R.drawable.mango,
R.drawable.orange,
R.drawable.watermelon};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
// Binding the ListView of activity_main.xml file
// with this java code in MainActivity.java
listView = findViewById(R.id.listView);
// creating an ArrayList of HashMap.The kEY of the HashMap
// is a String and VALUE is of any datatype(Object)
ArrayList<HashMap<String, Object>> list = new ArrayList<>();
// By a for loop, entering different types of data in HashMap,
// and adding this map including it's datas into the ArrayList
// as list item and this list is the second parameter of the SimpleAdapter
for (int i = 0; i < fruitNames.length; i++) {
// creating an Object of HashMap class
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
// Data entry in HashMap
map.put("fruitName", fruitNames[i]);
map.put("fruitImage", fruitImageIds[i]);
// adding the HashMap to the ArrayList
list.add(map);
}
// creating A string type array(from) which contains
// column names for each View in each row of the list
// and this array(form) is the fourth parameter of the SimpleAdapter
String[] from = {"fruitName", "fruitImage"};
// creating an integer type array(to) which contains
// id of each View in each row of the list
// and this array(form) is the fifth parameter of the SimpleAdapter
int to[] = {R.id.textView, R.id.imageView};
// creating an Object of SimpleAdapter class and
// passing all the required parameters
SimpleAdapter simpleAdapter = new SimpleAdapter(getApplicationContext(), list, R.layout.list_row_items, from, to);
// now setting the simpleAdapter to the ListView
listView.setAdapter(simpleAdapter);
}
}
我的锅
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import android.os.Bundle
import android.widget.ListView
import android.widget.SimpleAdapter
import java.util.ArrayList
import java.util.HashMap
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var listView:ListView
// creating a String type array
// (fruitNames) which contains
// names of different fruits' images
private val fruitNames=arrayOf("Banana","Grape","Guava","Mango","Orange","Watermelon")
// creating an Integer type array (fruitImageIds) which
// contains IDs of different fruits' images
private val fruitImageIds=arrayOf(R.drawable.banana,
R.drawable.grape,
R.drawable.guava,
R.drawable.mango,
R.drawable.orange,
R.drawable.watermelon)
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
// ViewBinding the ListView of activity_main.xml file
// with this kotlin code in MainActivity.kt
listView=findViewById(R.id.listView)
// creating an ArrayList of HashMap.The kEY of the HashMap is
// a String and VALUE is of any datatype(Any)
val list=ArrayList<HashMap<String,Any>>()
// By a for loop, entering different types of data in HashMap,
// and adding this map including it's datas into the ArrayList
// as list item and this list is the second parameter of the SimpleAdapter
for(i in fruitNames.indices){
val map=HashMap<String,Any>()
// Data entry in HashMap
map["fruitName"] = fruitNames[i]
map["fruitImage"]=fruitImageIds[i]
// adding the HashMap to the ArrayList
list.add(map)
}
// creating A string type array(from) which contains
// column names for each View in each row of the list
// and this array(form) is the fourth parameter of the SimpleAdapter
val from=arrayOf("fruitName","fruitImage")
// creating an integer type array(to) which contains
id of each View in each row of the list
and this array(form) is the fifth parameter of the SimpleAdapter*/
val to= intArrayOf(R.id.textView,R.id.imageView)
// creating an Object of SimpleAdapter
// class and passing
// all the required parameters
val simpleAdapter=SimpleAdapter(this,list,R.layout.list_row_items,from,to)
// now setting the simpleAdapter
// to the ListView
listView.adapter = simpleAdapter
}
}
因此,SimpleAdapter 保存数据并将数据发送到适配器视图,然后该视图可以从适配器视图中获取数据,并在我们之前创建的 ListView 上显示数据。
*请注意,您必须在 Java 和 Kotlin 之间选择任何一种语言作为特定项目的主要活动* * ***
*输出:*
